Sensual sweet seduction: Why chocolate is good for your heart, brain, and mood
05/01/2018 / By Janine Acero

People from all over the world collectively consume more than three million tons of cocoa beans a year, according to the World Cocoa Foundation.
Chocolate comes from the fruit of the Theobroma cacao tree, whose name means “food of the gods” in Greek, an apt name for the most popular sweet treat in the world. Theobroma cacao is native to the Amazon and Orinoco river basins in South America. These tropical trees thrive in hot, humid places within about 20 degrees of the equator. Growers have established plantations in other regions including West Africa and Southeast Asia. Today, Ghana, Côte d’Ivoire, Nigeria, Indonesia and Brazil, to keep up with the growing demand for the sweet commodity.
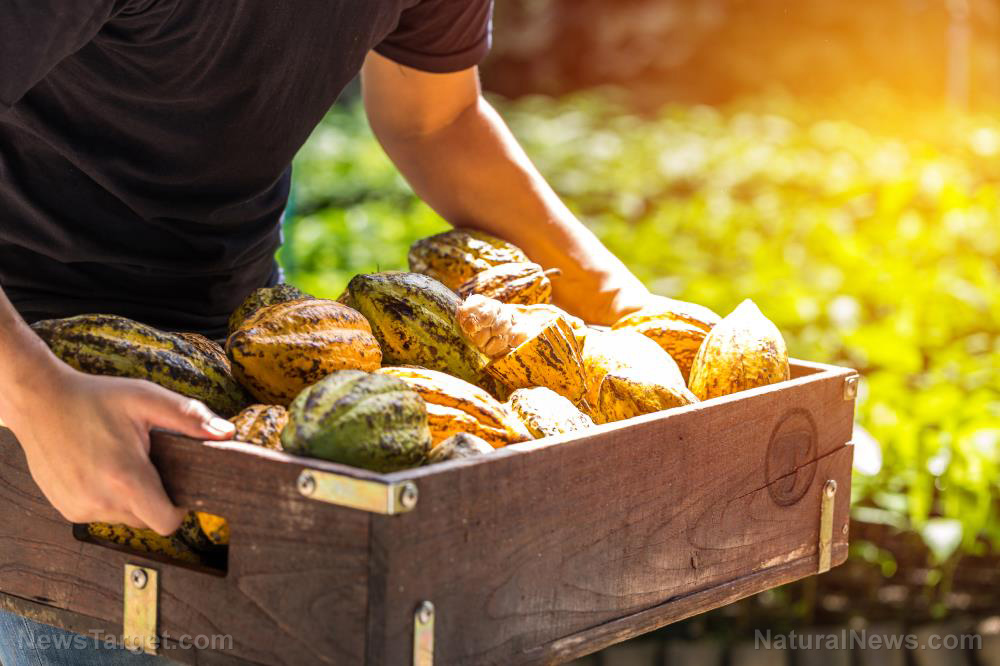
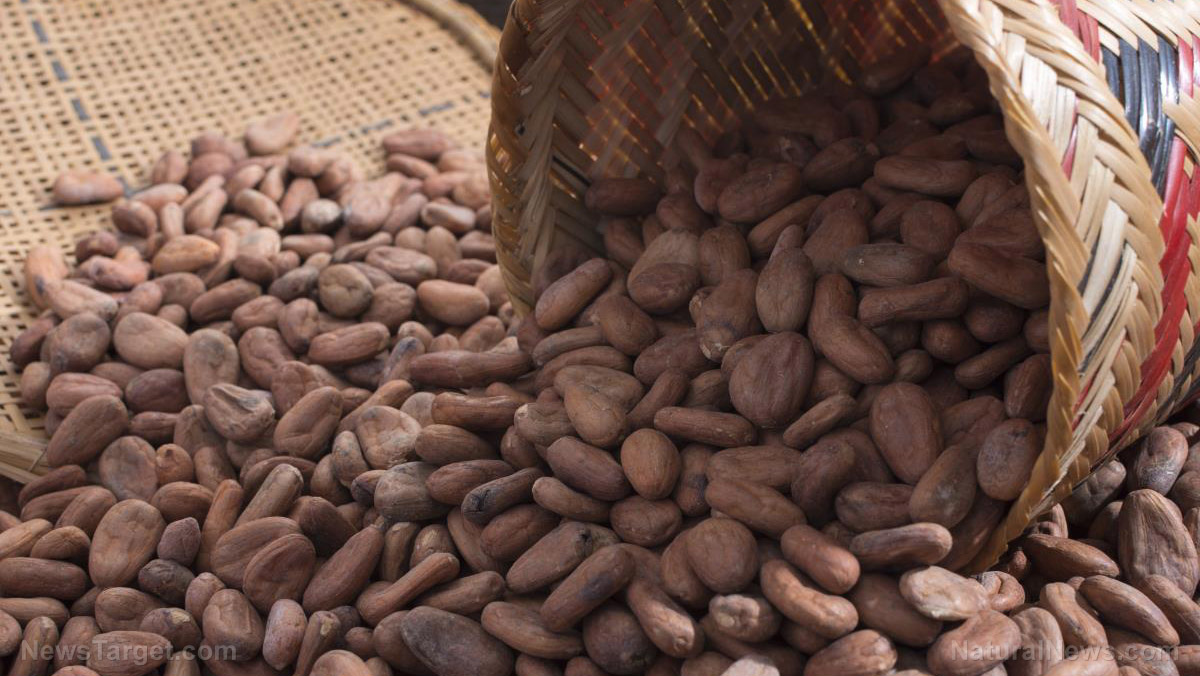
Cacao trees bear fruit that contains up to 50 seeds, or beans. Harvesting cacao seeds is done by hand because machines could injure the precious trees. Workers remove the pods when ripe, and open them with a machete. The seeds are placed in large fermentation trays that are stacked and covered in banana leaves, where they are left for two to seven days. The fermentation process produces the chocolate flavor and aroma.
The fermented beans are then dried out in the sun. Workers turn them several times a day for three to five days to complete drying. The beans are then taken to the chocolate factory, where they are cleaned and debris is removed.
The beans are roasted in large, rotating ovens. Roasting draws out the cocoa flavor of the beans. After roasting, the beans go into a winnowing machine, which cracks the beans and removes the hulls. The remaining part of the bean is the nib, which then becomes the chocolate.
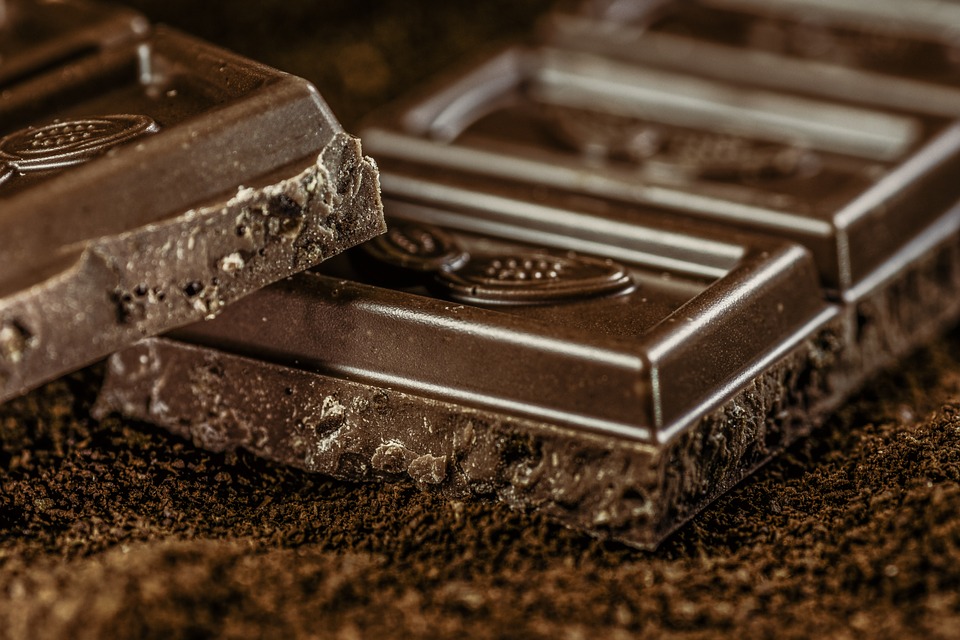
The nibs are ground under a series of rollers, and eventually turn into a thick paste called chocolate liquor. This paste does not contain alcohol – that would be chocolate liqueur. Chocolate liquor is the main source of unsweetened baking chocolate.
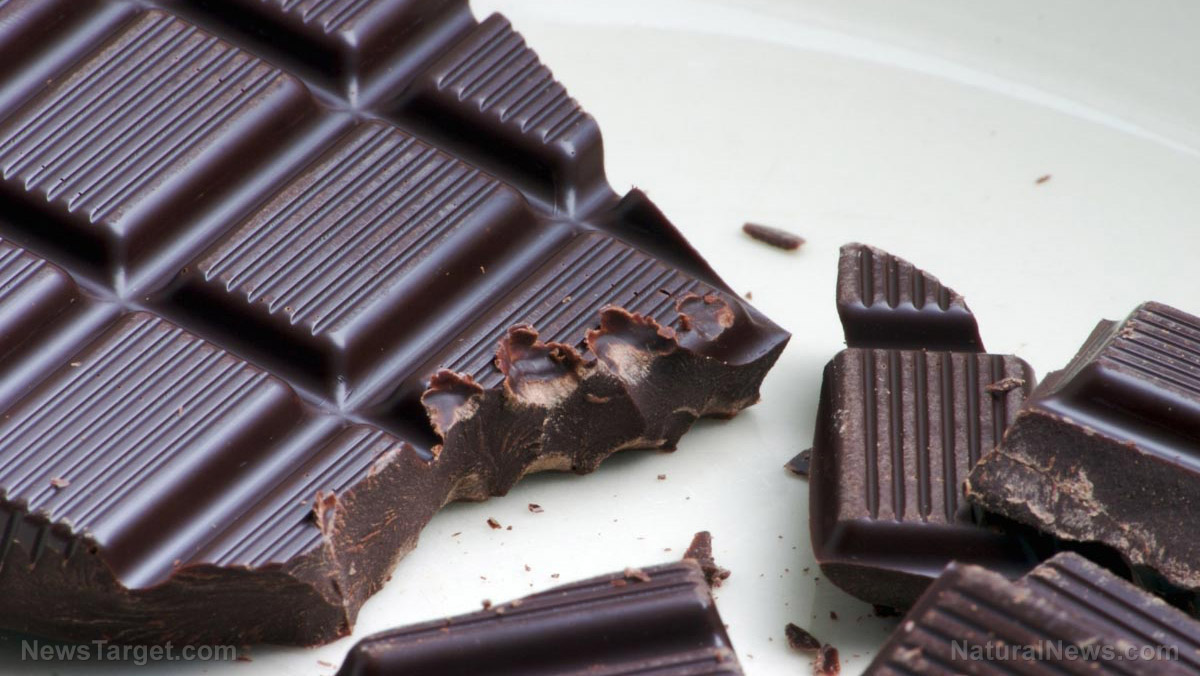
At this stage, the makers determine the type of chocolate being produced. The following are the types of chocolate:
- Unsweetened chocolate
- Bittersweet (extra dark) chocolate
- Semisweet (dark) chocolate
- Sweet chocolate
- Milk chocolate
- White chocolate
Why chocolate is good for you
Chocolate isn’t just a popular dessert, it also offers health benefits. Here are its three main health benefits; note that the following have been mostly associated with moderate consumption of chocolate.
- Heart food – Cacao beans are full of phytonutrients, which act as antioxidants. Cacao beans are also rich in iron, copper, magnesium, zinc and phosphorus. Dark chocolate especially contains two to three times more beneficial flavanols because they lack additional sugars that are added to other types of chocolate. Studies suggest that eating an ounce of chocolate at least five times a week may help prevent the risk of heart attack and heart failure. Chocolate may also help prevent the development of atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat) which increases the risk of heart failure, stroke and more.
- Brain food – Some studies have focused on chocolate’s ability to improve cognitive function. Studies suggest that those who ate a moderate amount of chocolate – on average, one chocolate snack a week, decreased their risk of cognitive decline by 40 percent over two years.
- Mood food – Chocolate is often associated with positive effects on mood, although this benefit remains debatable. According to the Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science, chocolate contains substances that stimulate the brain such as anandamines, tyramine, and phenylethylamine. However, these substances were found in very low concentrations – too low to induce an antidepressant effect. Still, chocolate is known to induce a positive shift in mood, especially when you eat some after a stressful day.
Find out more feel-good benefits of chocolate at Chocolate.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: bittersweet chocolate, Cacao, cacao beans, cacao butter, cacao liquor, cacao nibs, cacao production, cacao seeds, cacao trees, Chocolate, chocolate liquor, cocoa, dark chocolate, food of the gods, milk chocolate, phytonutrients, semisweet chocolate, Theobroma cacao, unsweetened chocolate, white chocolate, World Cocoa Foundation