Zinc can protect against oxidative stress when it’s taken together with chocolate and tea
02/04/2019 / By Zoey Sky

The human body needs zinc to remain healthy. A study published in the journal Nature Chemistry suggests that the nutritional benefits of zinc can be bolstered when combined with a natural compound found in chocolate and tea.
In particular, the study suggests that the trace mineral zinc may help activate an organic molecule that can prevent oxidative stress, which is linked to aging and a low life expectancy.
Zinc and oxidative stress
During the course of the study, researchers from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) and Dr. Christian Goldsmith, a professor from Auburn University in Alabama, found that zinc protects against superoxide that causes oxidative stress.
Superoxide is a byproduct of human cell respiration and it damages the body’s own biomolecules, like proteins, lipids, and even the human genome. Experts believe that superoxide has a role in the aging process and various illnesses like cancer, inflammation, or neurodegenerative diseases.
For zinc to work, the scientists determined that it must be taken together with a component found in food and beverages like chocolate, coffee, and wine. (Related: 15 foods that contain zinc, an essential mineral.)
This crucial component is a hydroquinone group found in polyphenols, which are plant substances that are responsible for smell and taste. The researchers explained that zinc activates hydroquinone, which produces a natural protection against superoxide.
Hydroquinone alone is unable to break down superoxide. But once zinc and hydroquinone are combined, they form a metal complex that imitates a superoxide dismutase enzyme (SOD). These enzymes can protect the body from the degradation processes triggered by oxidation. SODs also have an antioxidative effect.
Through these processes, the superoxide can be metabolized, which prevents damage to the organism. This, in turn, prevents oxidative stress.
This study is the first of its kind to copy the function of zinc without reverting to redox-active transition metals, like copper, iron, manganese, or nickel. The researchers stress that while these other metals could also have an antioxidative effect, any benefits they can offer are negated by the fact that taking too much can ironically increase oxidative stress.
The researchers posit that since zinc is not as toxic as the transition metals mentioned above, it can be used to produce new medication or supplements that will have considerably fewer side effects. Zinc could also be added to food that naturally contains hydroquinone to boost the consumer’s health.
Dr. Ivana Ivanovi-Burmazovi, Chair of Bioinorganic Chemistry at FAU, concluded, “It is certainly possible that wine, coffee, tea or chocolate may well become be available in future with added zinc. However, any alcohol content whatsoever would destroy the positive effects of this combination.”
Natural food sources of zinc
A diet that contains a healthy amount of zinc can boost your immune system and promote faster wound healing. The average adult female will need at least eight milligrams (mg) of zinc daily. Men will need at least 11 mg to maintain overall health.
Help your body fight off various diseases and infections by consuming more of the foods below that contain this crucial trace mineral.
- Crab and lobster – Crab and lobster are both good sources of zinc. A three-ounce serving of Alaskan king crab contains 43 percent (6.5 mg) while lobster has 23 percent (3.4 mg) of the recommended daily value.
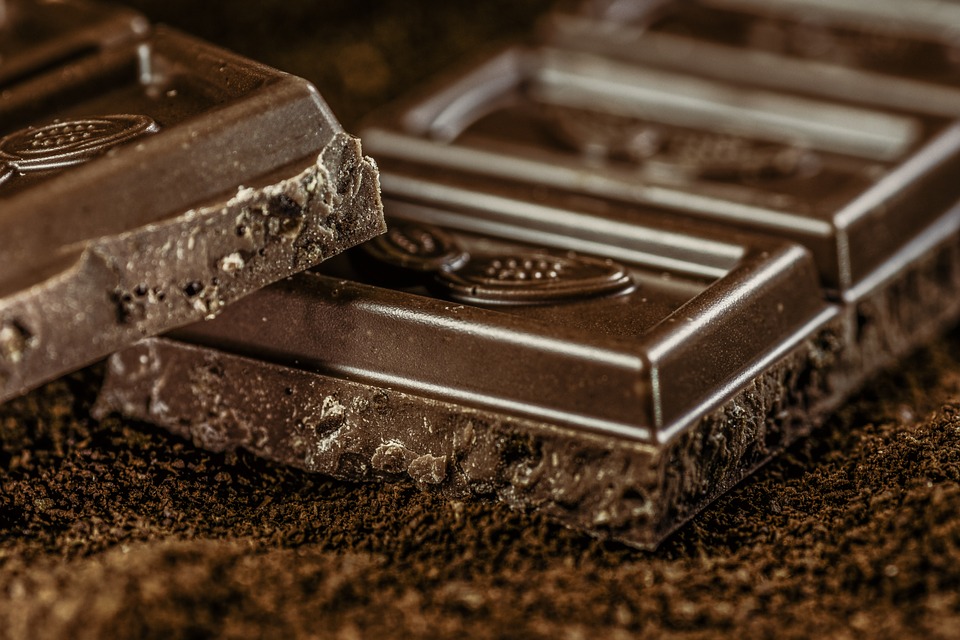
- Dark chocolate – Dark chocolate with 60 to 69 percent cacao has about five percent (0.8 mg) of the recommended daily value per ounce, while 70 to 85 percent cacao varieties have around six percent (0.9 mg).
- Meat and poultry – Beef, chicken, and pork all contain zinc. Eat nutritious cuts of lean meats with any visible fat removed, or skinless poultry. A three-ounce serving of roasted, skinless chicken breast has six percent (0.9 mg) of the daily recommended value of zinc.
- Oysters – A medium-sized oyster contains at least 5.3 mg of zinc. Relatively low in calories, oysters are also full of protein and other vitamins and minerals, like vitamins B-12 and C, iron, and selenium.
Read more articles about zinc and other essential minerals at Nutrients.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: aging, Chocolate, hydroquinone, natural cures, nutrients, nutrition, oxidative stress, prevention, superoxide, supplements, tea, trace minerals, zinc